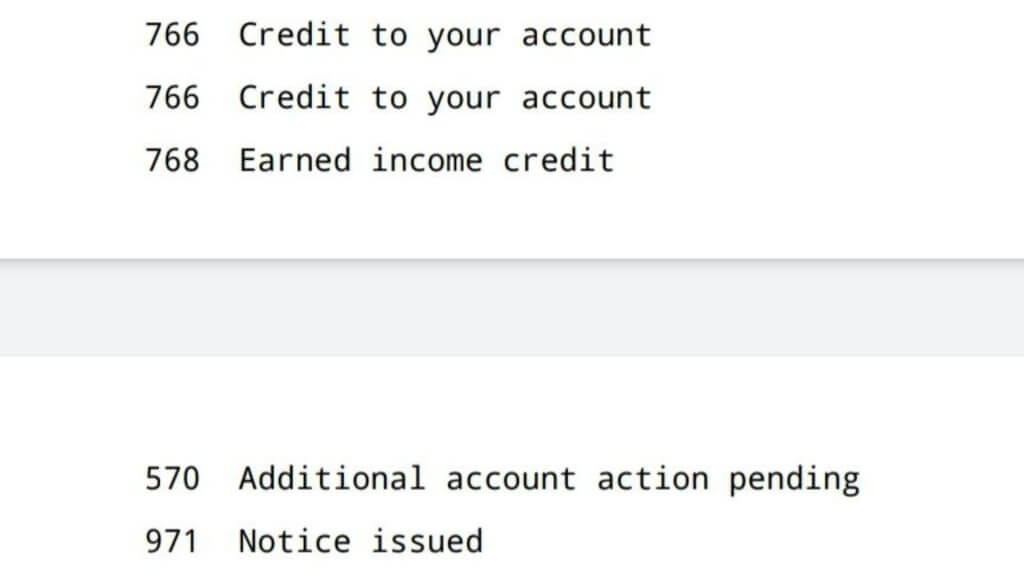
IRS Code 766
This article will tell you more about IRS Code 766, shedding light on its purpose, implications, and the steps taxpayers can take to address and potentially mitigate the effects of a tax refund offset.

Contents
It is important for taxpayers to understand what IRS Code 766 entails and how to comply with this provision to avoid potential penalties and other negative consequences. In this article, we will discuss what IRS Code 766 is, who is subject to it, how it works, the consequences of violating it, and how taxpayers can comply with this provision. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plays a significant role in enforcing tax laws and ensuring that taxpayers comply with their tax obligations. One important provision in the tax code is IRS Code 766, which requires taxpayers to file their tax returns by the due date, including extensions. Failure to comply with this provision can lead to serious consequences, such as penalties, interest, and other financial implications.
Who is subject to IRS Code 766?
All taxpayers who are required to file a tax return are subject to IRS Code 766 if they fail to file their tax return by the due date, including extensions. This includes individuals, corporations, partnerships, and other entities that are required to file a tax return.
If a taxpayer fails to file their tax return by the due date, including extensions, the IRS will assess a penalty under IRS Code 766. The penalty is calculated as a percentage of the unpaid tax due, up to a maximum of 25% of the unpaid tax. The penalty is assessed for each month or part of a month that the tax return is late, up to a maximum of five months. The penalty will continue to accrue until the tax return is filed or until the penalty reaches the maximum amount.
What are the Consequences of Violating IRS Code 766?
The consequences of violating IRS Code 766 can be significant. Taxpayers who fail to file their tax return on time may be subject to a penalty of up to 25% of the unpaid tax due. In addition, interest will accrue on the unpaid tax and penalty until the tax is paid in full. Failure to file a tax return can also result in other penalties and consequences, such as the loss of certain tax credits or the inability to obtain a loan.
How Can Taxpayers Comply with IRS Code 766?
The best way for taxpayers to comply with IRS Code 766 is to file their tax return by the due date, including extensions. Taxpayers who are unable to file their tax return by the due date should request an extension to avoid the late filing penalty. If a taxpayer is unable to pay their tax liability in full, they should still file their tax return on time to avoid the late filing penalty and then explore payment options with the IRS, such as an installment agreement.

FAQs
What is IRS Code 766?
IRS Code 766 is a provision in the tax code that requires taxpayers to file their tax returns by the due date, including extensions.
Who is subject to IRS Code 766?
All taxpayers who are required to file a tax return are subject to IRS Code 766 if they fail to file their tax return by the due date, including extensions.
What happens if a taxpayer violates IRS Code 766?
Taxpayers who fail to file their tax return on time may be subject to penalties, interest, and other financial consequences.
How can taxpayers comply with IRS Code 766?
Taxpayers can comply with IRS Code 766 by filing their tax return by the due date, including extensions. If a taxpayer is unable to file their tax return on time, they should request an extension to avoid the late filing penalty.