IRS Code 290
IRS Code 290 refers to the specific section of the Internal Revenue Code that relates to the assessment of additional taxes, penalties, and interest. This article will tell you understand what you need to know about IRS Code 290.

IRS Code 290, known as “Additional Tax Assessments,” plays a significant role in the Internal Revenue Service’s efforts to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. This particular code relates to the assessment of additional taxes, penalties, and interest on taxpayers’ accounts. Understanding IRS Code 290, who receives it, and why it appears on tax transcripts is essential for taxpayers to navigate potential tax liabilities and take appropriate actions.
Reasons for Receiving IRS Code 290 on Transcripts
- Audits and Examinations: Taxpayers who undergo an IRS audit or examination may receive IRS Code 290 if the examination identifies errors, unreported income, or discrepancies in the original tax return.
- Amended Returns: When a taxpayer submits an amended tax return, the IRS may use Code 290 to assess additional taxes, penalties, and interest based on the revised information provided.
- Underreported Income: If the IRS identifies unreported income or discrepancies in income reported by third parties (e.g., employers, financial institutions), they may assess additional taxes using Code 290.
- Disallowed Deductions or Credits: Taxpayers who claim deductions or credits that the IRS deems ineligible or unsupported may receive Code 290 assessments for the disallowed amounts.
- Noncompliance or Late Filing: Individuals or businesses who fail to file their tax returns, file late, or exhibit noncompliance with tax laws may be subject to Code 290 assessments for penalties and interest.
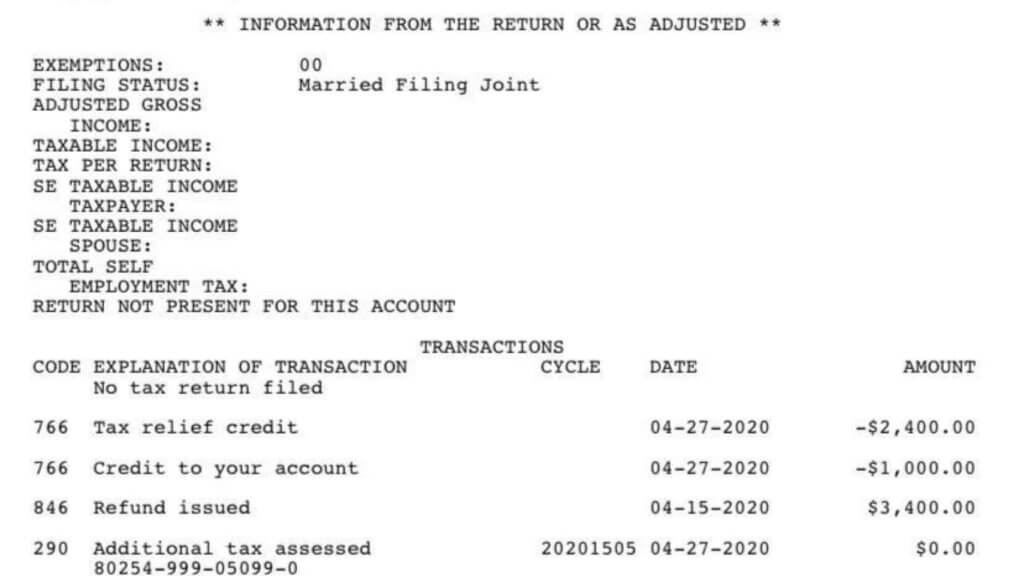
Actions to Take After IRS Code 290
- Thoroughly review the tax transcript to understand the nature of the additional tax assessments, penalties, and interest imposed.
- Consult a tax professional or a certified public accountant (CPA) to analyze the transcript, identify potential errors, and determine the best course of action.
- Address any compliance issues identified, such as filing late returns, correcting errors, or paying the assessed amounts promptly to avoid further penalties and interest.
- If you believe that the Code 290 assessments are inaccurate or unjustified, explore options for dispute resolution, such as filing an appeal with the IRS or requesting a reconsideration of the assessed amounts.





